Table Of Content
FGF5 is a key inducer of catagen and FGF5-deficient mice have a prolonged anagen phase. In addition to FGF5, TGF-β1, IL-1b, the neurotrophins NT-3, NT-4 and BMP2/4 and TNF-α have been described to induce catagen [36]. Moreover the follicular papilla is an essential source of growth factors [1, 3, 16, 28]. Through the anagen I–V, hair stem cells proliferate, encloses the dermal papilla, grow downwards to the skin and begin to proliferate hair shaft and IRS, respectively. This phase can last up to 6–8 years in hair follicles [1, 11, 18].
Hair Growth
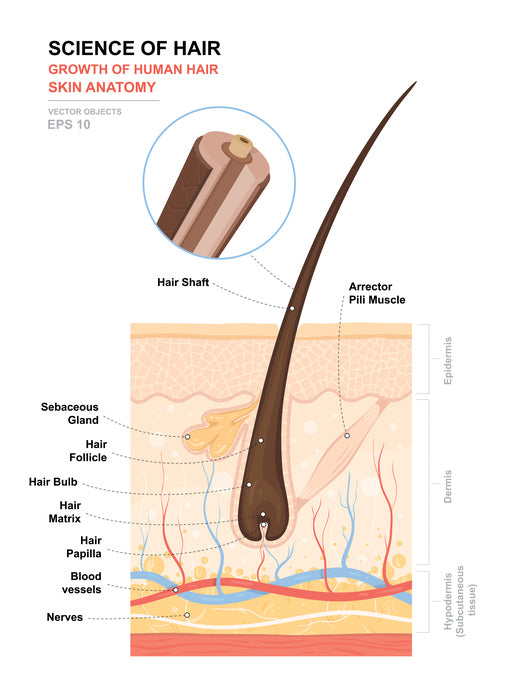
The most important one of these glands is the sebaceous gland, which produces and secretes the natural oils lubricating hairs, namely sebum. So, the hair under a light microscope shows two important features – hair shaft and hair follicle. The important features of the hair shaft are the cuticle, cortex, and medulla, which you might identify with the help of a light microscope.
Structure of hair shaft under a microscope
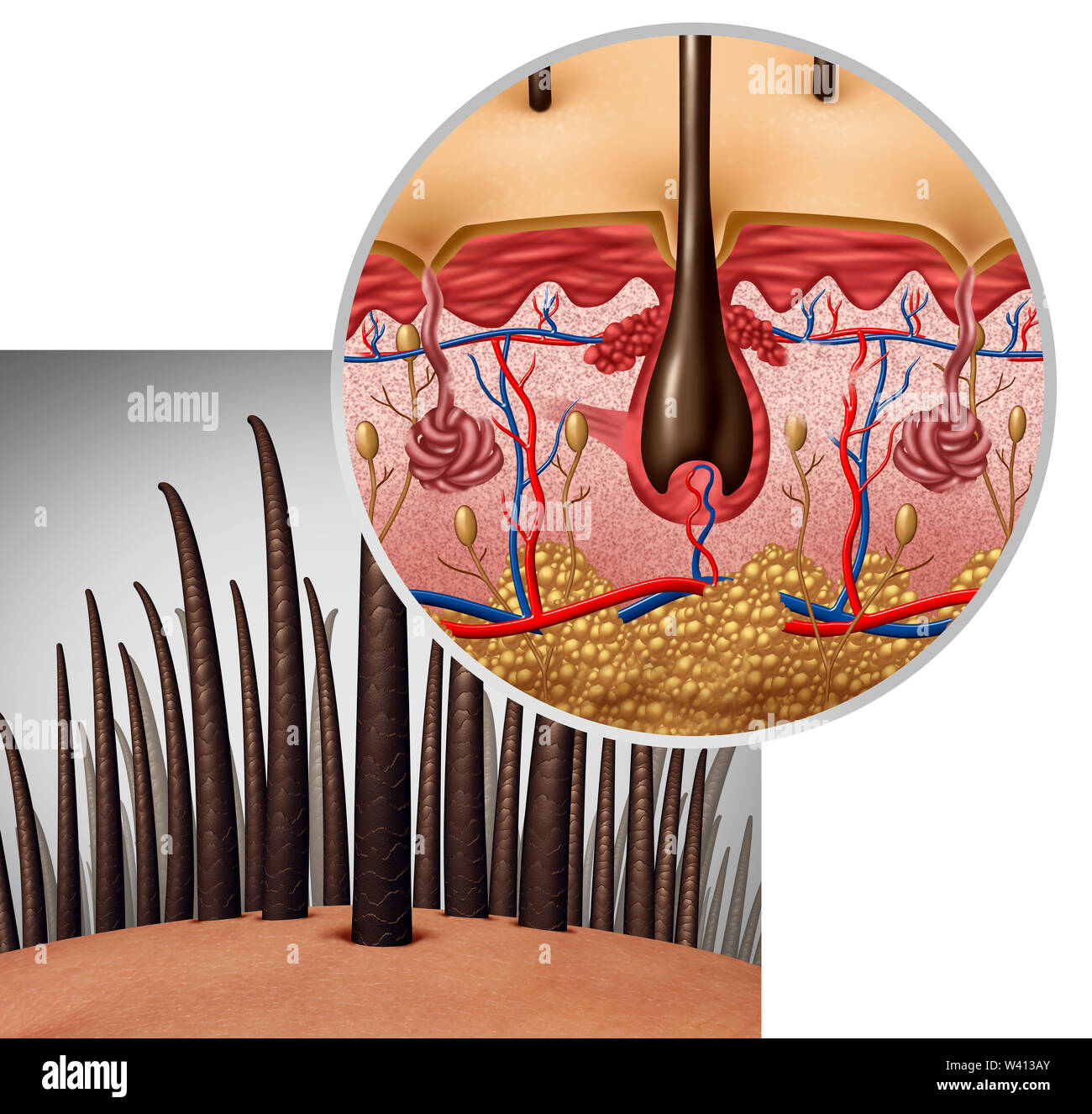
It has several types of stem cells, which develop into specialized cells and can renew themselves over a long period of time. The base of the root of a cat’s hair shows a frayed fibrils appearance. In the labeled diagram of the cat’s hair, I tried to show some of the important features from the hair shaft and follicle. You will find numerous blood vessels and numerous connective tissue fibers in the connective tissue of the hair follicle. These numerous vessels and fibers form the basket-like network around the lower end of the hair follicle. The outer layer of the hair follicle starts from the cuboidal cells of the outer layer and continues with the stratum spinosum of the skin.
Anatomy and Physiology of Hair
The cellular or vacuolated medulla are most common in many animal species. All these uniserial, multiserial, cellular or vacuolated, and lattice medulla are shown in the hair labeled diagrams. All these types of medulla of hair are shown on the labeled diagrams. The appearance of the medulla of different types of hair is different.
From bleach blonde hair color to the trendiest hair accessories we will try anything to make our crowns stand out. Our hair grows in so many different shades, places, hair textures, and types, that everyone’s mane is naturally unique. But when it comes to hair anatomy, all of our strands are essentially the same. A piece of hair may look simple, but it’s one of the body's most complicated structures. The hair follicle is the part below the skin, and the hair shaft is what you see above your skin.
Structure of Hair
But the root of the cat hair is elongated and does not possess any distinct shape. Let’s see some of the common and important features of the hairs from other different parts of an animal’s body. The hair may be straight, curly, and kinly in different animal species.
What Is Human Hair Made Of?
Telogen effluvium describes a disruption in the normal hair growth and rest cycles that results in excessive shedding and hair loss. This condition can be precipitated by physical stress, such as surgery or malnutrition, or by medical exposure, such as chemotherapy and common medications. The hair shaft is the portion of your hair that projects from your scalp. The root of each hair is located in a follicle, which is embedded in the skin and nourished by the blood vessels in the dermis (see diagram). In a young adult, scalp follicles typically spend 6 to 8 years in anagen, 2 to 3 weeks in catagen, and 1 to 3 months in telogen. Scalp hairs grow at a rate of about 1 mm per 3 days (10–18 cm/yr) in the anagen phase.
Other features of hair follicles under a microscope
Hair follicle melanocytes and their precursors reside in the hair matrix and along the outer root sheath of anagen hair follicles. Melanin synthesis is established in lysosome-related organelles named melanosomes. In the precortical matrix, these melanosomes are transferred to the hair shaft keratinocytes and formed a pigmented hair shaft. The hair follicle also contains melanocyte stem cells, which are located in the bulge and in the secondary hair [33–35]. At any given time, about 90% of the scalp follicles are in the anagen stage.
Scars Mended Using Transplanted Hair Follicles - Neuroscience News
Scars Mended Using Transplanted Hair Follicles.
Posted: Fri, 06 Jan 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
During catagen the proximal of the hair shaft is keratinized and forms the club hair, whereas the distal part of the follicle is involuted by apoptosis [16, 38]. In humans, it pulls the follicles into a vertical position and causes “goose bumps,” but serves no useful purpose. The hair follicles in your skin contain living cells to allow your hair to grow. The shaft—the part of the hair we see—is made up of dead cells and consists of three different layers. As a piece of hair grows, it goes through three phases before it sheds and a new one grows. Again, this diagram shows different layers of rounded nucleated cells that form the outer root layer of the hair follicle.
A hair follicle consists of two main layers, an inner (epithelial) root sheath and an outer (fibrous) root sheath. At the base of the hair follicle is the hair bulb, which houses the dermal papillae and hair matrix cells. It is formed from dermal connective tissue, supplies blood to the epithelial sheath and holds undifferentiated hair stem cells. The cells of the hair follicle actively change during the growth cycle of a hair. The isthmus is the lower portion of the upper part of hair follicle between the opening of the sebaceous gland and the insertion of arrector pili muscle.
But, these spinous or petal-like scales are not found in the human hair shaft. The hair shaft under a microscope shows three different distinct layers – an inner medulla, a cortex, and an outer cuticle. The structure of a pencil may be a good analogy for the structure of a hair shaft. The cells rupture to secrete an oily secretion into the lumen of the hair follicle. Again, the ruptured cells are continuously replaced by stem cells located at the edges of the glands. Again, let’s see the cross-section of the hair follicles and try to identify the following features from the labeled diagram.
The first is the anagen phase, during which cells divide rapidly at the root of the hair, pushing the hair shaft up and out. The length of this phase is measured in years, typically from 2 to 7 years. The catagen phase lasts only 2 to 3 weeks, and marks a transition from the hair follicle’s active growth. Finally, during the telogen phase, the hair follicle is at rest and no new growth occurs. At the end of this phase, which lasts about 2 to 4 months, another anagen phase begins. The basal cells in the hair matrix then produce a new hair follicle, which pushes the old hair out as the growth cycle repeats itself.
This is the largest number of hair follicles you will ever have. As long as new hair cells continue to grow in the hair bulb, the hair continues to grow longer. At any point in time, about 90 percent of a person’s total amount of hair is in this growth phase. The first diagram of the hair shows the full structure of the skin.
A club hair may fall out during catagen or telogen, or as it is pushed out by the new hair in the next anagen phase. The cylindrical shaft of the hair under a microscope shows three layers (medulla, cortex, and cuticle) of keratinized cells. Again, the terminal end of the hair follicle shows an expanded hair bulb composed of connective tissue papilla and hair root. Hair under a microscope shows a hair follicle and a cylindrical hair shaft. In a hair shaft, you will find columns of keratinized cells organized into three layers – medulla, cortex, and cuticle.

No comments:
Post a Comment